CODEX ALIMENTARIUS COMMISSION
ABOUT CODEX
The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) is an international food standards body established jointly by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) of the United Nations in May 1963 with the objective of protecting consumer health and ensuring fair practices in food trade.
The Agreement on Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) of the World Trade Organization (WTO) recognizes Codex standards, guidelines and recommendations as reference standards for international trade and trade dispute settlement. Currently, the Codex Alimentarius Commission has 189 Codex Members made up of 188 Member Countries and 1 Member Organization (The European Union). Bhutan became a member of Codex Alimentarius in 1999.
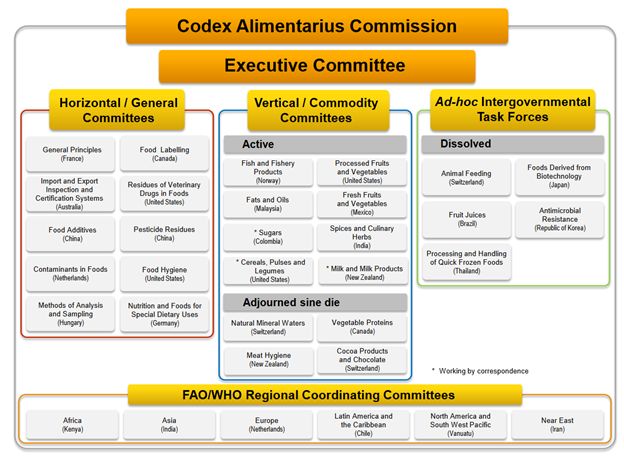
CODEX COMMITTEES
The food standards development work of the Commission is assisted by its Executive Committee and subsidiary bodies –General subject/Commodity Committees, Coordinating Committees and Task Forces. [+]
Executive Committee of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CCEXEC)
The Executive Committee acts on behalf of the Commission as its executive organ and assists in the management of its programme of standards development, mainly by conducting a critical review of its work programme, making proposals regarding general orientation and strategic planning.
India, as the Regional Coordinator for FAO/WHO Regional Coordinating Committee for Asia (CCASIA) is a member of the CCEXEC”
Subsidiary bodies
- Committees, which prepare draft standards for submission to the Commission; may be either General Subject or Commodity specific
- Coordinating Committees , through which regions or groups of countries coordinate food standards activities in the region, including the development of regional standards. Currently there are six Codex regions.
- Task Forces , ad hoc Intergovernmental Task force with very limited terms of reference established for a fixed period of time.
Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance with an objective of developing guidance on the management of foodborne antimicrobial resistance is currently active.
CODEX TEXTS
“Voluntary in nature, Codex standards can be general or specific and are recognized by WTO Agreements as reference standards”
General Standards, Guidelines and Codes of Practice
These core Codex texts, typically deal with hygienic practice, labelling, contaminants, additives, inspection & certification, nutrition and residues of veterinary drugs and pesticides and apply horizontally to products and product categories.
Commodity standards
Codex commodity standards refer to a specific product although increasingly Codex now develops standards for food groups.
Regional standards
Standards developed by the respective Regional Coordinating Committees, applicable to the respective regions.
The list of adopted standards and other texts can be available here
For more information, please visit http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/en/